
Metabolic health has become a central focus in both public health and preventive nutrition. It refers to the optimal functioning of physiological systems involved in blood sugar regulation, lipid metabolism, blood pressure control, and body composition. When these systems are disrupted, they can lead to chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
One of the most prevalent clinical manifestations of this systemic imbalance is metabolic syndrome, a cluster of interconnected risk factors that includes abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and elevated blood glucose. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), it affects more than 25% of the global adult population¹. This condition increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes by two to five times, even in individuals with a normal body mass index.
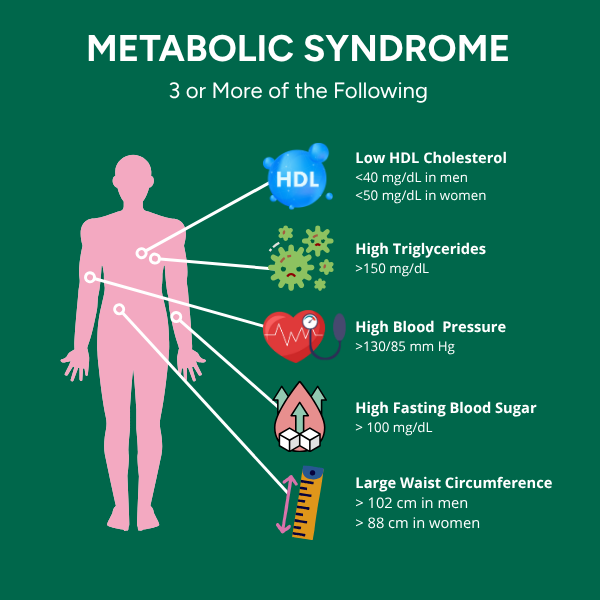
Metabolic syndrome is diagnosed when at least three out of five established criteria are met: increased waist circumference, elevated triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, and elevated fasting glucose. This definition, adopted by the NCEP ATP III and the IDF, allows early identification of individuals at risk, even before overt disease has developed.
Metabolic Syndrome: More Than Just Excess Weight
Although it is often associated with overweight or obesity, metabolic syndrome can also occur in individuals with a normal weight, particularly those with insulin resistance or high levels of visceral fat. Contributing factors include physical inactivity, diets rich in refined sugars and saturated fats, chronic stress, and poor sleep.
In recent years, the role of the gut microbiota has gained attention due to its influence on intestinal permeability, low-grade inflammation, and energy balance. This broader understanding has reshaped how prevention and intervention strategies are approached, incorporating physiological dimensions previously overlooked in clinical practice.
A Broader, Integrated Approach
Managing metabolic syndrome requires a comprehensive and sustained intervention strategy. Lifestyle improvements, such as dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, better sleep, and stress management, are essential. At the same time, natural bioactive ingredients backed by scientific evidence are emerging as valuable complementary tools, especially for at-risk populations or individuals with early metabolic dysfunction.
Current research is focusing on compounds that can act on multiple physiological pathways at once, improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, supporting liver function, and restoring intestinal balance. This multifactorial perspective is particularly relevant in a condition like metabolic syndrome, where several systems are simultaneously affected.
The Role of Nutraceuticals: Science and Prevention
Nutraceuticals, natural bioactive compounds with documented health benefits, are increasingly valued for their potential to support metabolic balance. Their strength lies in the combination of efficacy, safety, and traceability, particularly when their composition is standardized and scientifically validated.
Unlike compounds with a single mode of action, many nutraceuticals exert synergistic effects across multiple metabolic pathways. Botanical extracts, for instance, have been shown to reduce triglyceride levels, modulate inflammatory markers, improve liver enzyme profiles, or reinforce gut barrier integrity. The key is to ensure that their activity is well characterized and reproducible.
Csat®: Preclinical Evidence in a Metabolic Syndrome Model
A prime example of this approach is Csat®, a standardized carob (Ceratonia siliqua) extract developed by Pharmactive. Its activity has been assessed in an in vivo model of diet-induced metabolic syndrome².
In a study published in Antioxidants (2022), mice treated with Csat showed marked improvements in lipid profiles—especially a reduction in triglycerides—along with lower weight gain and decreased fat mass. The treatment also positively influenced liver function and inflammatory markers, while contributing to the partial restoration of intestinal barrier integrity.
This multifaceted profile positions Csat+ as a promising ingredient for nutraceutical formulations that aim to support metabolic health through a natural and evidence-based approach.

Do you want to know more about Csat?? Clic here.

